Kia Optima Hybrid: Exhaust Emission Control System / CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) System Description and Operation
| Description |
| – |
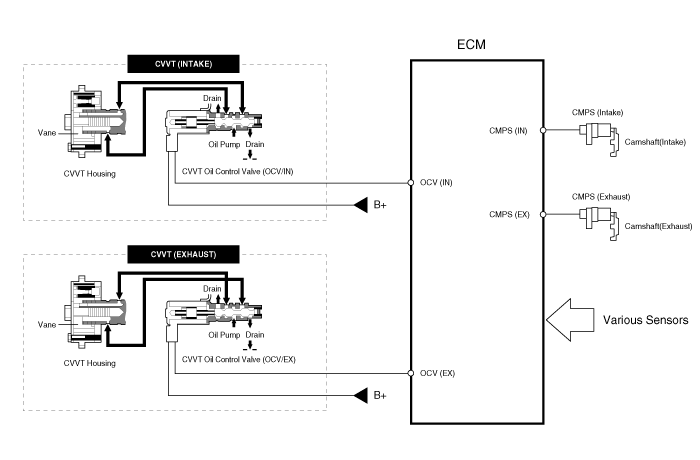
the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine
oil to the cam phaser or runs out the engine oil from the cam phaser in
accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal, |
| – |
and the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil. |
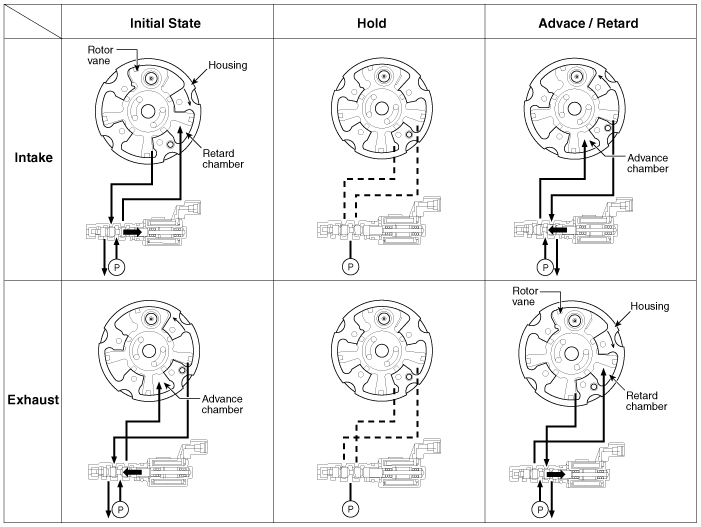
| Operation Principle |
| [CVVT System Mode] |
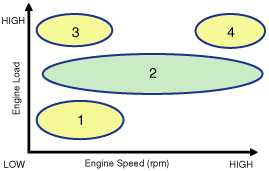
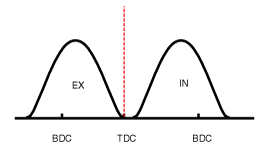
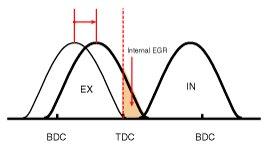
| (1) Low Speed / Low Load | (2) Part Load |
|
|
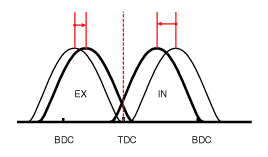
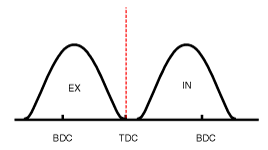
| (3) Low Speed / High Load | (4) High Speed / High Load |
|
|
| Driving Condition | Exhaust Valve | Intake Valve | ||
| Valve Timing | Effect | Valve Timing | Effect | |
| (1) Low Speed /Low Load | Completely Advance | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability | Completely Retard | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
| (2) Part Load | Retard | * Increase of expansion work * Reduction of pumping loss * Reduction of HC | Retard | * Reduction of pumping loss |
| (3) Low Speed /High Load | Retard | * Increase of expansion work | Advance | * Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
| (4) High Speed /High Load | Advance | * Reduction of pumping loss | Retard | * Improvement of volumetric efficiency |
 Catalytic Converter Description and Operation
Catalytic Converter Description and Operation
Description The catalytic converter of the gasoline engine is a three way catalyst. It oxidizes carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons (HC), and separates oxygen from the oxides of nitrogen (NOx). ...
Other information:
Kia Optima Hybrid (TF HEV) 2016-2020 Service Manual: NVLD(Natural Vacuum Leakage Detection) Description and Operation
Description NVLD(Natural Vacuum Leakage Detection) is located between the canister and the fuel tank air filter. NVLD is to detect leaks equivalent to a 0.5 mm hole in the fuel tank, canister and hoses. When the engine has been running, the temperature of the fuel in the fuel tank is raised slightly. ...
Kia Optima Hybrid (TF HEV) 2016-2020 Service Manual: Windshield Glass Repair procedures
Replacement Removal • Put on gloves to protect your hands. • Use seat covers to avoid damaging any surfaces. 1. Remove the following items. • Front pillar trim (Refer to the BD group - "Interior Trim") • ECM mirror (Refer to the BD group - "Mirror") • Rain sensor (Refer to the ...