Kia Optima Hybrid: AHB(Active Hydraulic Boost) System / Rear Disc Brake Repair procedures
Kia Optima Hybrid (TF HEV) 2016-2020 Service Manual / Brake System / AHB(Active Hydraulic Boost) System / Rear Disc Brake Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. |
Remove the rear wheel & tire.
|
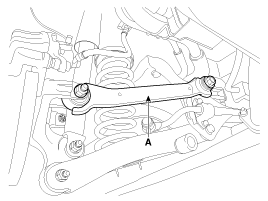
| 2. |
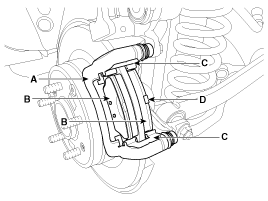
Remove the rear upper arm (A).
|
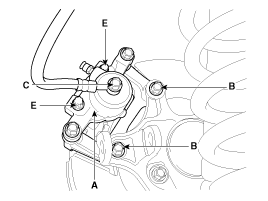
| 3. |
Loosen the hose eyebolt (C) and caliper mounting bolts (B), then remove the rear caliper assembly (A).
|
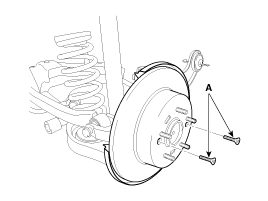
| 4. |
Remove the rear brake disc by loosening the screws (A).
|
| Replacement |
Rear brake pads
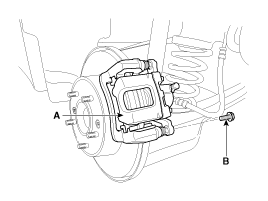
| 1. |
Loosen the guide rod bolt (B) and pivot the caliper (A) up out of the way.
|
| 2. |
Replace pad shim (D), pad retainers (C) and brake pads (B) in the caliper carrier (A).
|
| Inspection |
Rear Brake Disc Thickness Check
| 1. |
Check the brake pads for wear and fade. |
| 2. |
Check the brake disc for damage and cracks. |
| 3. |
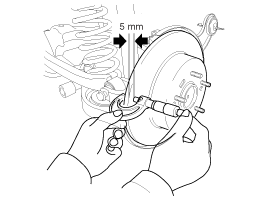
Remove all rust and contamination from the surface, and
measure the disc thickness at 8 points, at least, of same distance (5mm)
from the brake disc outer circle.
|
| 4. |
If wear exceeds the limit, replace the discs and pad assembly left and right of the vehicle. |
Rear Brake Pad Check
| 1. |
Check the pad wear. Measure the pad thickness and replace it, if it is less than the specified value.
|
| 2. |
Check that grease is applied, to sliding contact points. Check for metal damage to the pad and backing.
|
Rear Brake Disc Runout Check
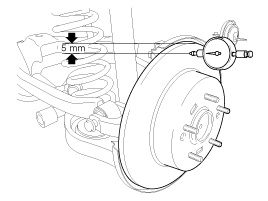
| 1. |
Place a dial gauge about 5mm (0.2 in.) from the outer circumference of the brake disc, and measure the runout of the disc.
|
| 2. |
If the runout of the brake disc exceeds the limit specification, replace the disc, and then measure the runout again. |
| 3. |
If the runout does not meet the limit specification, remove
the disc, turn it 180° and reinstall. Then check the runout of the
brake disc again. |
| 4. |
If the runout cannot be corrected by changing the position of the brake disc, replace the brake disc. |
| Installation |
| 1. |
Installation is the reverse of removal. |
| 2. |
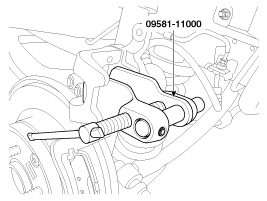
Use a SST (09581-11000) when installing the brake caliper assembly.
|
| 3. |
After installation, bleed the brake system.
(Refer to Brake system bleeding) |
|
 Rear Disc Brake Components and Components Location
Rear Disc Brake Components and Components Location
Components 1. Guide rod bolt2. Bleed screw3. Caliper carrier4. Caliper body5. Inner pad shim6. Brake pad7. Pad retainer ...
Other information:
Kia Optima Hybrid (TF HEV) 2016-2020 Service Manual: Engine Clutch Control Solenoid Valve (E/C_VFS) Specifications
Specifications Direct control VFS [E/C] Control type : Normal low type Control Pressure kpa(kgf/cm?, psi)9.81 ~ 500.14(0.1 ~ 5.1, 1.42 ~ 72.54)Current value (mA)50~850 Internal resistance (?)5.1 ...
Kia Optima Hybrid (TF HEV) 2016-2020 Service Manual: Description and Operation
Description The Vehicle Information System is a Telematics service that ensures comfortable and enjoyable driving by providing safety, security, and vehicle diagnostic information, with the option of using your smartphone. The term "Telematics" is a combination of telecommunication and ...
© 2025 Copyright www.koptimatfhev.com